Before a name and symbol are approved, an element may be referred to by its atomic number (e.g., element 120) or by its systematic element name. The systematic element name is a temporary name that is based on the atomic number as a root and the -ium ending as a suffix. For example, element 120 has the temporary name unbinilium. 3 Li Lithium 6.941. Atomic Number: 3. Atomic Weight: 6.941. Melting Point: 453.65 K (180.50°C or 356.90°F) Boiling Point: 1615 K (1342°C or 2448°F) Density: 0.534 grams per cubic centimeter. Phase at Room Temperature: Solid. Element Classification: Metal. Period Number: 2. Group Number: 1. Group Name: Alkali Metal. What's in a name? The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of He 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
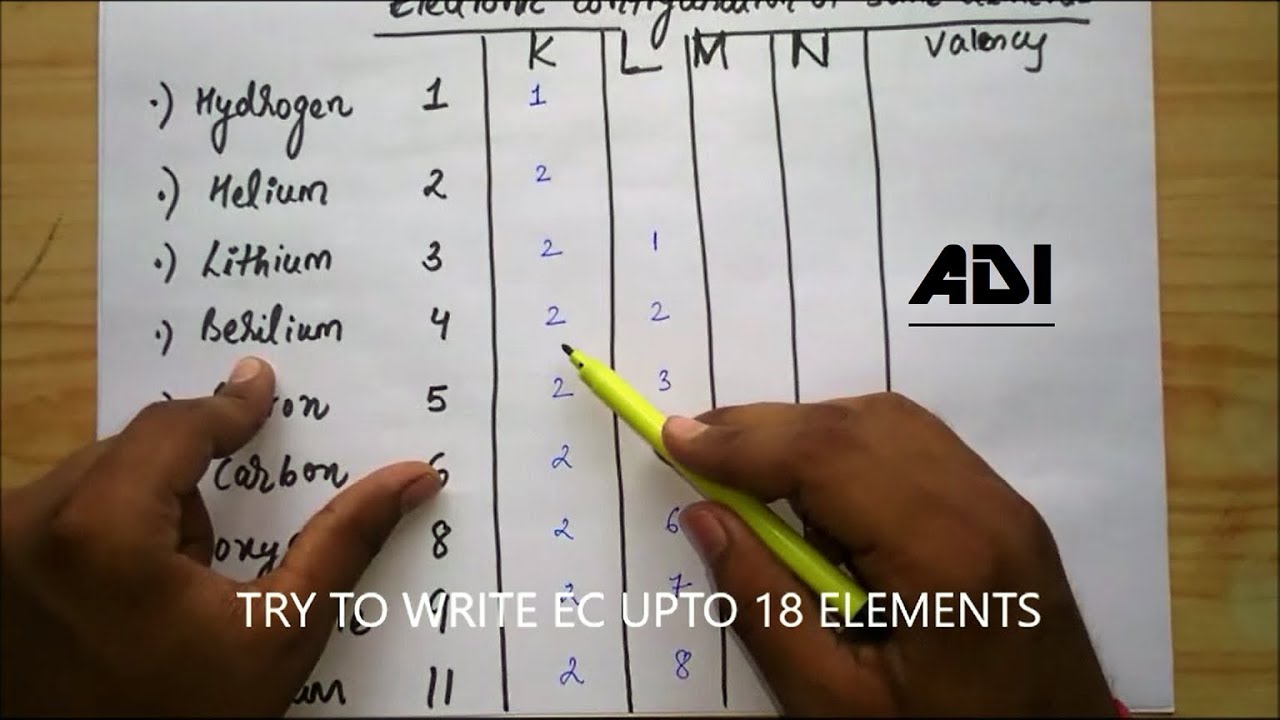
Atomic Number of Lithium is 3.
Chemical symbol for Lithium is Li. Number of protons in Lithium is 3. Atomic weight of Lithium is 6.94 u or g/mol. Melting point of Lithium is 180,5 °C and its the boiling point is 1317 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery YearAbout Lithium

Named after the Greek word meaning stone, Lithium is a soft metal, with the lowest density of all metals in the Periodic Table. Therefore, it can be quite easily cut with a knife and is almost as light as wood. Lithium does not occur in its pure form in nature but can be found in a number of minerals. Lithium is toxic; it is an alkali metal which easily reacts with water producing lithium hydroxide, used as an agent to absorb carbon dioxide. A very important usage if lithium is in batteries, especially rechargeable ones for our modern communication devices. For a variety of usages, lithium is alloyed with the metals like aluminum, magnesium, and other metals.
Uses of Lithium
Lithium which is the lightest metallic element is used in heat transfer applications, and as a scavenger in metallurgy. Many nonmetallic elements are scavenged by lithium. Because of its high electrode potential, lithium is also used as the negative electrode in nonrechargeable lithium batteries. Today rechargeable lithium batteries are commonly used for cell phones, cameras, and lots of other devices. There is another general usage of lithium in ceramics and glass industry. Lithium oxide, an inorganic chemical compound with lithium and oxide ions, is used as a flux in ceramic glazes.
Lithium is also commonly used in greases, in metallurgy, in flares and pyrotechnics, etc. Lithium hydroxide and lithium peroxide are used as carbon dioxide removal and air purification in spacecraft and submarines too.
Compounds with Lithium
- LiH: Lithium hydride
- LiCl: Lithium chloride
- LiF: Lithium fluoride
- Li2S: Lithium sulphide
- Lil: Lithium iodide
- Li2CO3: Lithium carbonate
- LiNO2: Lithium nitrite
- LiCoO2: Lithium cobalt oxide
- LiOH: Lithium hydroxide
- Li2O: Lithium oxide
- LiBr: Lithium bromide
- C4H6LiNO4: Lithium aspartate
- Li2SiO3: Lithium metasilicate
Properties of Lithium Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 3 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Symbol | Li |
| Group | 1 |
| Period | 2 |
| Atomic Weight | 6.94 u |
| Density | 0.534 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point (K) | 453.69 K |
| Melting Point (℃) | 180,5 °C |
| Boiling Point (K) | 1560 K |
| Boiling Point (℃) | 1317 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 3.582 J/g · K |
| Abundance | 20 mg/kg |
| State at STP | Solid |
| Occurrence | Primordial |
| Description | Alkali metal |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | 0.98 |
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 5.39172 |
| Atomic Radius | 145pm |
| Covalent Radius | 134pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 182 |
| Valence Electrons | 1 |
| Year of Discovery | 1817 |
| Discoverer | Arfvedson |
What is the Boiling Point of Lithium?

Lithium boiling point is 1317 °C. Boiling point of Lithium in Kelvin is 1560 K.
What is the Melting Point of Lithium?
Lithium melting point is 180,5 °C. Melting point of Lithium in Kelvin is 453.69 K.
How Abundant is Lithium?
Abundant value of Lithium is 20 mg/kg.
What is the State of Lithium at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
State of Lithium is Solid at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure.
When was Lithium Discovered?
Lithium was discovered in 1817.
Lithium Atomic Number Of Protons

Lithium Atomic Number And Symbol
